Global Health R&D Under Debate At World Health Assembly

What’s at stake for global health R&D during WHA 69? This was the question of the moment at a World Health Assembly side event panel yesterday. Image Credits: Mara Pillinger

Original news and analysis on international IP policy

What’s at stake for global health R&D during WHA 69? This was the question of the moment at a World Health Assembly side event panel yesterday. Image Credits: Mara Pillinger

The fight against epidemics cannot only rely on innovation, according to speakers at an event organised by the pharmaceutical industry alongside the annual World Health Assembly’s opening day. Strong health systems, collaboration of all stakeholders, preventive measures, and the ability to fund research are prerequisite to innovation, they said.

The World Health Assembly opened today with World Health Organization Director General Margaret Chan repeating that this year has a record number of agenda items and over 3,000 participants. She slapped at profit-seeking mechanisms leading to "slow-motion disasters," which put economic interests above concerns about well-being. In particular, she underlined the lack of research and development for antimicrobial treatments and the rise of chronic non-communicable diseases.

This year is profoundly important in humanity’s future ability to stave off resistance to antibiotics and other medicines, a top World Health Organization official said on the eve of this week’s annual World Health Assembly.
“Ever-Greening of Patents” has been an expression that has been extensively used in debates related to the global pharmaceutical industry at least since the last two decades. Interestingly, this term has never been statutorily defined and hence has been applied most freely by professionals, policy makers and politicians alike. It would be appropriate to objectively examine whether patents in any jurisdiction can ever be “ever-greened”. A fitting initiation to this debate is the very concept of what a patent is from the very first principles, writes Prabuddha Ganguli.
In the light of the UN High-Level Panel on Access to Medicines, this series of sponsored articles challenges experts to give their views on the policies that best support the development of solutions to societies’ greatest challenges and how enabling policy environments, including IP systems, influence the development and flow of new technologies and services in different sectors, fields of technology, and jurisdictions. The views expressed in the articles are those of the authors. Below is an interview with David Taylor, Professor of Pharmaceutical and Public Health Policy, University College London, UK.

Public health advocates last week told World Health Organization delegates they must act quickly to save the lives of poor populations suffering from less common diseases for which there is no research and development funding. Nongovernmental organisations showed up to a WHO meeting on the issue to urge on delegates, even holding a public demonstration in front of the UN, but there was concern afterward at the little progress made.

New technologies are of limited value if they are not accessible. Thus the crucial challenge lies not only in promoting innovation, but in translating innovation into social impact. This was the theme of the fourth Conference on Technologies for Development (“Tech4Dev”).
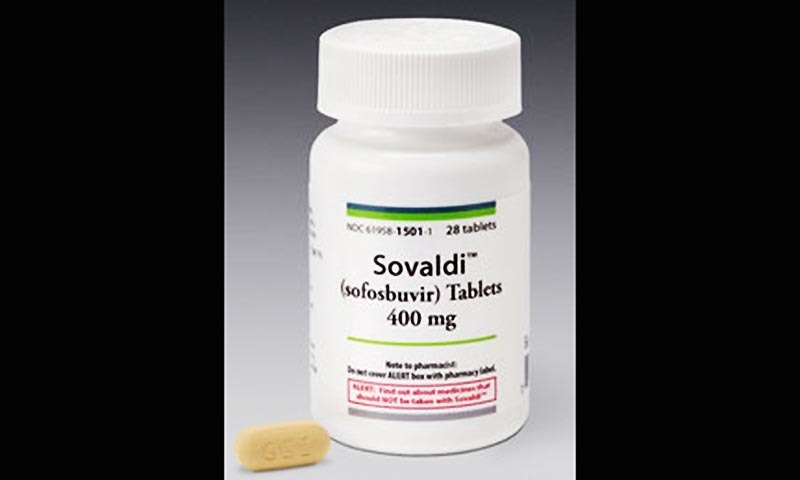
A copy of the new Indian patent office order shows the details of the decision to reverse an earlier direction and grant a patent in India on the high-value hepatitis C drug. [Updated with response from Gilead]

A number of World Health Organization member states attended a meeting last week aimed finding ways to sustainably finance research and development for medical products, especially those for poor populations lacking means to pay high prices. According to the outcome document and a WHO official, they heard many viewpoints from experts and made progress but much was left for the World Health Assembly later this month.